Are you following a strict gluten-free lifestyle; yet you still suffer from symptoms related to gluten?
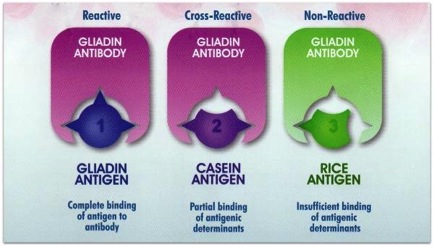
If so, it could be that you are eating foods that do not contain gluten but your body reacts to them as if they do. This process is called cross-reactivity.
There are a number of naturally gluten-free foods such as cheese, chocolate and coffee that contain proteins so similar to gluten that your body confuses them for gluten. When you eat these foods your body and immune system react as if you just ate a bowl of whole-wheat pasta.
It’s estimated that at least half of those who are gluten intolerant are also sensitive to dairy (cheese, yogurt, milk and butter) due to its cross-reactivity with gluten.
Image credit: www.healthnowmedical.com
Below is a list of common foods that cross-react with gluten:
- Amaranth
- Buckwheat
- Chocolate
- Coffee
- Corn
- Dairy ie Milk and Cheese (Alpha-Casein, Beta-Casein, Casomorphin, Butyrophilin, Whey Protein)
- Egg
- Hemp
- Millet
- Oats
- Polish wheat
- Potato
- Rice
- Sesame
- Sorghum
- Soy
- Tapioca
- Teff
- Yeast
If you are gluten-intolerant and you are still having health issues even after removing gluten from your diet, try eliminating the above foods for at least two months and see if your symptoms improve. Make sure you have healed your gut as well. Then, after two months you may reintroduce the above foods one at a time to determine which ones you are cross-reacting to, if any at all. Laboratory testing is also available to determine which foods are cross-reactive for you.
If you determine that there are foods that are cross-reactive for you, the treatment is to permanently remove these foods from your diet along with gluten. Remember, that though the cross-reactive foods do not actually contain gluten your body thinks they do and therefore the inflammation and damage to your body is equal to that of gluten.
Photo credit and original article published on MindBodyGreen